Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
/**
* Pure-PHP arbitrary precision integer arithmetic library.
*
* Supports base-2, base-10, base-16, and base-256 numbers. Uses the GMP or BCMath extensions, if available,
* and an internal implementation, otherwise.
*
* PHP version 5 and 7
*
* Here's an example of how to use this library:
* <code>
* <?php
* $a = new \phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger(2);
* $b = new \phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger(3);
*
* $c = $a->add($b);
*
* echo $c->toString(); // outputs 5
* ?>
* </code>
*
* @author Jim Wigginton <terrafrost@php.net>
* @copyright 2017 Jim Wigginton
* @license http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.html MIT License
*/
namespace phpseclib3\Math;
use phpseclib3\Exception\BadConfigurationException;
use phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger\Engines\Engine;
/**
* Pure-PHP arbitrary precision integer arithmetic library. Supports base-2, base-10, base-16, and base-256
* numbers.
*
* @author Jim Wigginton <terrafrost@php.net>
*/
class BigInteger implements \JsonSerializable
{
/**
* Main Engine
*
* @var class-string<Engine>
*/
private static $mainEngine;
/**
* Selected Engines
*
* @var list<string>
*/
private static $engines;
/**
* The actual BigInteger object
*
* @var object
*/
private $value;
/**
* Mode independent value used for serialization.
*
* @see self::__sleep()
* @see self::__wakeup()
* @var string
*/
private $hex;
/**
* Precision (used only for serialization)
*
* @see self::__sleep()
* @see self::__wakeup()
* @var int
*/
private $precision;
/**
* Sets engine type.
*
* Throws an exception if the type is invalid
*
* @param string $main
* @param list<string> $modexps optional
* @return void
*/
public static function setEngine($main, array $modexps = ['DefaultEngine'])
{
self::$engines = [];
$fqmain = 'phpseclib3\\Math\\BigInteger\\Engines\\' . $main;
if (!class_exists($fqmain) || !method_exists($fqmain, 'isValidEngine')) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException("$main is not a valid engine");
}
if (!$fqmain::isValidEngine()) {
throw new BadConfigurationException("$main is not setup correctly on this system");
}
/** @var class-string<Engine> $fqmain */
self::$mainEngine = $fqmain;
$found = false;
foreach ($modexps as $modexp) {
try {
$fqmain::setModExpEngine($modexp);
$found = true;
break;
} catch (\Exception $e) {
}
}
if (!$found) {
throw new BadConfigurationException("No valid modular exponentiation engine found for $main");
}
self::$engines = [$main, $modexp];
}
/**
* Returns the engine type
*
* @return string[]
*/
public static function getEngine()
{
self::initialize_static_variables();
return self::$engines;
}
/**
* Initialize static variables
*/
private static function initialize_static_variables()
{
if (!isset(self::$mainEngine)) {
$engines = [
['GMP', ['DefaultEngine']],
['PHP64', ['OpenSSL']],
['BCMath', ['OpenSSL']],
['PHP32', ['OpenSSL']],
['PHP64', ['DefaultEngine']],
['PHP32', ['DefaultEngine']]
];
foreach ($engines as $engine) {
try {
self::setEngine($engine[0], $engine[1]);
return;
} catch (\Exception $e) {
}
}
throw new \UnexpectedValueException('No valid BigInteger found. This is only possible when JIT is enabled on Windows and neither the GMP or BCMath extensions are available so either disable JIT or install GMP / BCMath');
}
}
/**
* Converts base-2, base-10, base-16, and binary strings (base-256) to BigIntegers.
*
* If the second parameter - $base - is negative, then it will be assumed that the number's are encoded using
* two's compliment. The sole exception to this is -10, which is treated the same as 10 is.
*
* @param string|int|BigInteger\Engines\Engine $x Base-10 number or base-$base number if $base set.
* @param int $base
*/
public function __construct($x = 0, $base = 10)
{
self::initialize_static_variables();
if ($x instanceof self::$mainEngine) {
$this->value = clone $x;
} elseif ($x instanceof BigInteger\Engines\Engine) {
$this->value = new static("$x");
$this->value->setPrecision($x->getPrecision());
} else {
$this->value = new self::$mainEngine($x, $base);
}
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a base-10 number.
*
* @return string
*/
public function toString()
{
return $this->value->toString();
}
/**
* __toString() magic method
*/
public function __toString()
{
return (string)$this->value;
}
/**
* __debugInfo() magic method
*
* Will be called, automatically, when print_r() or var_dump() are called
*/
public function __debugInfo()
{
return $this->value->__debugInfo();
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a byte string (eg. base-256).
*
* @param bool $twos_compliment
* @return string
*/
public function toBytes($twos_compliment = false)
{
return $this->value->toBytes($twos_compliment);
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a hex string (eg. base-16).
*
* @param bool $twos_compliment
* @return string
*/
public function toHex($twos_compliment = false)
{
return $this->value->toHex($twos_compliment);
}
/**
* Converts a BigInteger to a bit string (eg. base-2).
*
* Negative numbers are saved as positive numbers, unless $twos_compliment is set to true, at which point, they're
* saved as two's compliment.
*
* @param bool $twos_compliment
* @return string
*/
public function toBits($twos_compliment = false)
{
return $this->value->toBits($twos_compliment);
}
/**
* Adds two BigIntegers.
*
* @param BigInteger $y
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function add(BigInteger $y)
{
return new static($this->value->add($y->value));
}
/**
* Subtracts two BigIntegers.
*
* @param BigInteger $y
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function subtract(BigInteger $y)
{
return new static($this->value->subtract($y->value));
}
/**
* Multiplies two BigIntegers
*
* @param BigInteger $x
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function multiply(BigInteger $x)
{
return new static($this->value->multiply($x->value));
}
/**
* Divides two BigIntegers.
*
* Returns an array whose first element contains the quotient and whose second element contains the
* "common residue". If the remainder would be positive, the "common residue" and the remainder are the
* same. If the remainder would be negative, the "common residue" is equal to the sum of the remainder
* and the divisor (basically, the "common residue" is the first positive modulo).
*
* Here's an example:
* <code>
* <?php
* $a = new \phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger('10');
* $b = new \phpseclib3\Math\BigInteger('20');
*
* list($quotient, $remainder) = $a->divide($b);
*
* echo $quotient->toString(); // outputs 0
* echo "\r\n";
* echo $remainder->toString(); // outputs 10
* ?>
* </code>
*
* @param BigInteger $y
* @return BigInteger[]
*/
public function divide(BigInteger $y)
{
list($q, $r) = $this->value->divide($y->value);
return [
new static($q),
new static($r)
];
}
/**
* Calculates modular inverses.
*
* Say you have (30 mod 17 * x mod 17) mod 17 == 1. x can be found using modular inverses.
*
* @param BigInteger $n
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function modInverse(BigInteger $n)
{
return new static($this->value->modInverse($n->value));
}
/**
* Calculates modular inverses.
*
* Say you have (30 mod 17 * x mod 17) mod 17 == 1. x can be found using modular inverses.
*
* @param BigInteger $n
* @return BigInteger[]
*/
public function extendedGCD(BigInteger $n)
{
extract($this->value->extendedGCD($n->value));
/**
* @var BigInteger $gcd
* @var BigInteger $x
* @var BigInteger $y
*/
return [
'gcd' => new static($gcd),
'x' => new static($x),
'y' => new static($y)
];
}
/**
* Calculates the greatest common divisor
*
* Say you have 693 and 609. The GCD is 21.
*
* @param BigInteger $n
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function gcd(BigInteger $n)
{
return new static($this->value->gcd($n->value));
}
/**
* Absolute value.
*
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function abs()
{
return new static($this->value->abs());
}
/**
* Set Precision
*
* Some bitwise operations give different results depending on the precision being used. Examples include left
* shift, not, and rotates.
*
* @param int $bits
*/
public function setPrecision($bits)
{
$this->value->setPrecision($bits);
}
/**
* Get Precision
*
* Returns the precision if it exists, false if it doesn't
*
* @return int|bool
*/
public function getPrecision()
{
return $this->value->getPrecision();
}
/**
* Serialize
*
* Will be called, automatically, when serialize() is called on a BigInteger object.
*
* __sleep() / __wakeup() have been around since PHP 4.0
*
* \Serializable was introduced in PHP 5.1 and deprecated in PHP 8.1:
* https://wiki.php.net/rfc/phase_out_serializable
*
* __serialize() / __unserialize() were introduced in PHP 7.4:
* https://wiki.php.net/rfc/custom_object_serialization
*
* @return array
*/
public function __sleep()
{
$this->hex = $this->toHex(true);
$vars = ['hex'];
if ($this->getPrecision() > 0) {
$vars[] = 'precision';
}
return $vars;
}
/**
* Serialize
*
* Will be called, automatically, when unserialize() is called on a BigInteger object.
*/
public function __wakeup()
{
$temp = new static($this->hex, -16);
$this->value = $temp->value;
if ($this->precision > 0) {
// recalculate $this->bitmask
$this->setPrecision($this->precision);
}
}
/**
* JSON Serialize
*
* Will be called, automatically, when json_encode() is called on a BigInteger object.
*
* @return array{hex: string, precision?: int]
*/
#[\ReturnTypeWillChange]
public function jsonSerialize()
{
$result = ['hex' => $this->toHex(true)];
if ($this->precision > 0) {
$result['precision'] = $this->getPrecision();
}
return $result;
}
/**
* Performs modular exponentiation.
*
* @param BigInteger $e
* @param BigInteger $n
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function powMod(BigInteger $e, BigInteger $n)
{
return new static($this->value->powMod($e->value, $n->value));
}
/**
* Performs modular exponentiation.
*
* @param BigInteger $e
* @param BigInteger $n
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function modPow(BigInteger $e, BigInteger $n)
{
return new static($this->value->modPow($e->value, $n->value));
}
/**
* Compares two numbers.
*
* Although one might think !$x->compare($y) means $x != $y, it, in fact, means the opposite. The reason for this
* is demonstrated thusly:
*
* $x > $y: $x->compare($y) > 0
* $x < $y: $x->compare($y) < 0
* $x == $y: $x->compare($y) == 0
*
* Note how the same comparison operator is used. If you want to test for equality, use $x->equals($y).
*
* {@internal Could return $this->subtract($x), but that's not as fast as what we do do.}
*
* @param BigInteger $y
* @return int in case < 0 if $this is less than $y; > 0 if $this is greater than $y, and 0 if they are equal.
* @see self::equals()
*/
public function compare(BigInteger $y)
{
return $this->value->compare($y->value);
}
/**
* Tests the equality of two numbers.
*
* If you need to see if one number is greater than or less than another number, use BigInteger::compare()
*
* @param BigInteger $x
* @return bool
*/
public function equals(BigInteger $x)
{
return $this->value->equals($x->value);
}
/**
* Logical Not
*
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_not()
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_not());
}
/**
* Logical And
*
* @param BigInteger $x
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_and(BigInteger $x)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_and($x->value));
}
/**
* Logical Or
*
* @param BigInteger $x
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_or(BigInteger $x)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_or($x->value));
}
/**
* Logical Exclusive Or
*
* @param BigInteger $x
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_xor(BigInteger $x)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_xor($x->value));
}
/**
* Logical Right Shift
*
* Shifts BigInteger's by $shift bits, effectively dividing by 2**$shift.
*
* @param int $shift
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_rightShift($shift)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_rightShift($shift));
}
/**
* Logical Left Shift
*
* Shifts BigInteger's by $shift bits, effectively multiplying by 2**$shift.
*
* @param int $shift
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_leftShift($shift)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_leftShift($shift));
}
/**
* Logical Left Rotate
*
* Instead of the top x bits being dropped they're appended to the shifted bit string.
*
* @param int $shift
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_leftRotate($shift)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_leftRotate($shift));
}
/**
* Logical Right Rotate
*
* Instead of the bottom x bits being dropped they're prepended to the shifted bit string.
*
* @param int $shift
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function bitwise_rightRotate($shift)
{
return new static($this->value->bitwise_rightRotate($shift));
}
/**
* Returns the smallest and largest n-bit number
*
* @param int $bits
* @return BigInteger[]
*/
public static function minMaxBits($bits)
{
self::initialize_static_variables();
$class = self::$mainEngine;
extract($class::minMaxBits($bits));
/** @var BigInteger $min
* @var BigInteger $max
*/
return [
'min' => new static($min),
'max' => new static($max)
];
}
/**
* Return the size of a BigInteger in bits
*
* @return int
*/
public function getLength()
{
return $this->value->getLength();
}
/**
* Return the size of a BigInteger in bytes
*
* @return int
*/
public function getLengthInBytes()
{
return $this->value->getLengthInBytes();
}
/**
* Generates a random number of a certain size
*
* Bit length is equal to $size
*
* @param int $size
* @return BigInteger
*/
public static function random($size)
{
self::initialize_static_variables();
$class = self::$mainEngine;
return new static($class::random($size));
}
/**
* Generates a random prime number of a certain size
*
* Bit length is equal to $size
*
* @param int $size
* @return BigInteger
*/
public static function randomPrime($size)
{
self::initialize_static_variables();
$class = self::$mainEngine;
return new static($class::randomPrime($size));
}
/**
* Generate a random prime number between a range
*
* If there's not a prime within the given range, false will be returned.
*
* @param BigInteger $min
* @param BigInteger $max
* @return false|BigInteger
*/
public static function randomRangePrime(BigInteger $min, BigInteger $max)
{
$class = self::$mainEngine;
return new static($class::randomRangePrime($min->value, $max->value));
}
/**
* Generate a random number between a range
*
* Returns a random number between $min and $max where $min and $max
* can be defined using one of the two methods:
*
* BigInteger::randomRange($min, $max)
* BigInteger::randomRange($max, $min)
*
* @param BigInteger $min
* @param BigInteger $max
* @return BigInteger
*/
public static function randomRange(BigInteger $min, BigInteger $max)
{
$class = self::$mainEngine;
return new static($class::randomRange($min->value, $max->value));
}
/**
* Checks a numer to see if it's prime
*
* Assuming the $t parameter is not set, this function has an error rate of 2**-80. The main motivation for the
* $t parameter is distributability. BigInteger::randomPrime() can be distributed across multiple pageloads
* on a website instead of just one.
*
* @param int|bool $t
* @return bool
*/
public function isPrime($t = false)
{
return $this->value->isPrime($t);
}
/**
* Calculates the nth root of a biginteger.
*
* Returns the nth root of a positive biginteger, where n defaults to 2
*
* @param int $n optional
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function root($n = 2)
{
return new static($this->value->root($n));
}
/**
* Performs exponentiation.
*
* @param BigInteger $n
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function pow(BigInteger $n)
{
return new static($this->value->pow($n->value));
}
/**
* Return the minimum BigInteger between an arbitrary number of BigIntegers.
*
* @param BigInteger ...$nums
* @return BigInteger
*/
public static function min(BigInteger ...$nums)
{
$class = self::$mainEngine;
$nums = array_map(function ($num) {
return $num->value;
}, $nums);
return new static($class::min(...$nums));
}
/**
* Return the maximum BigInteger between an arbitrary number of BigIntegers.
*
* @param BigInteger ...$nums
* @return BigInteger
*/
public static function max(BigInteger ...$nums)
{
$class = self::$mainEngine;
$nums = array_map(function ($num) {
return $num->value;
}, $nums);
return new static($class::max(...$nums));
}
/**
* Tests BigInteger to see if it is between two integers, inclusive
*
* @param BigInteger $min
* @param BigInteger $max
* @return bool
*/
public function between(BigInteger $min, BigInteger $max)
{
return $this->value->between($min->value, $max->value);
}
/**
* Clone
*/
public function __clone()
{
$this->value = clone $this->value;
}
/**
* Is Odd?
*
* @return bool
*/
public function isOdd()
{
return $this->value->isOdd();
}
/**
* Tests if a bit is set
*
* @param int $x
* @return bool
*/
public function testBit($x)
{
return $this->value->testBit($x);
}
/**
* Is Negative?
*
* @return bool
*/
public function isNegative()
{
return $this->value->isNegative();
}
/**
* Negate
*
* Given $k, returns -$k
*
* @return BigInteger
*/
public function negate()
{
return new static($this->value->negate());
}
/**
* Scan for 1 and right shift by that amount
*
* ie. $s = gmp_scan1($n, 0) and $r = gmp_div_q($n, gmp_pow(gmp_init('2'), $s));
*
* @param BigInteger $r
* @return int
*/
public static function scan1divide(BigInteger $r)
{
$class = self::$mainEngine;
return $class::scan1divide($r->value);
}
/**
* Create Recurring Modulo Function
*
* Sometimes it may be desirable to do repeated modulos with the same number outside of
* modular exponentiation
*
* @return callable
*/
public function createRecurringModuloFunction()
{
$func = $this->value->createRecurringModuloFunction();
return function (BigInteger $x) use ($func) {
return new static($func($x->value));
};
}
/**
* Bitwise Split
*
* Splits BigInteger's into chunks of $split bits
*
* @param int $split
* @return BigInteger[]
*/
public function bitwise_split($split)
{
return array_map(function ($val) {
return new static($val);
}, $this->value->bitwise_split($split));
}
}
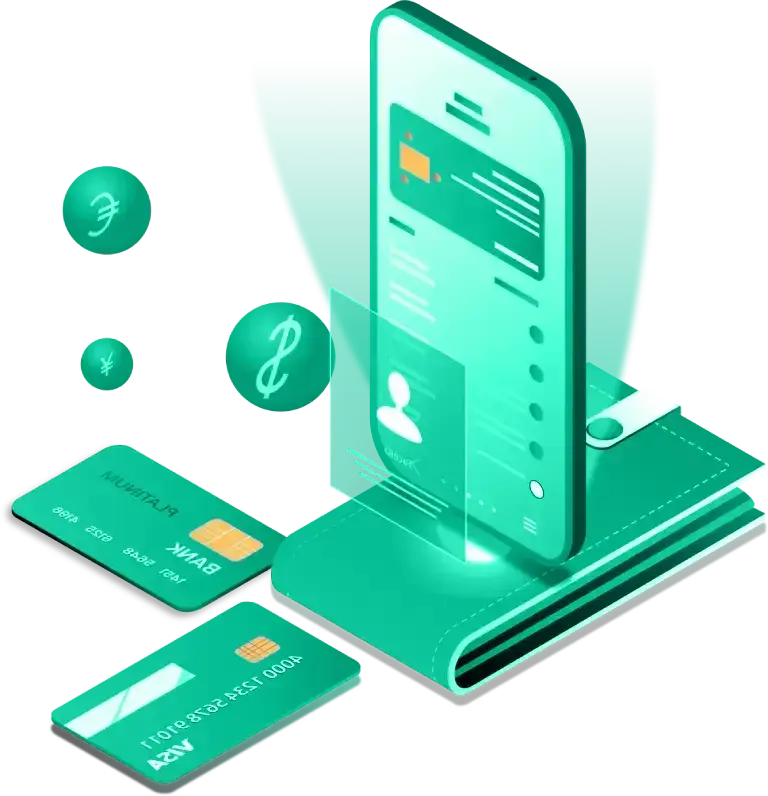
How it Works

Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
