Proven Expertise
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace Cron;
use DateTime;
use DateTimeImmutable;
use DateTimeInterface;
use DateTimeZone;
use Exception;
use InvalidArgumentException;
use LogicException;
use RuntimeException;
use Webmozart\Assert\Assert;
/**
* CRON expression parser that can determine whether or not a CRON expression is
* due to run, the next run date and previous run date of a CRON expression.
* The determinations made by this class are accurate if checked run once per
* minute (seconds are dropped from date time comparisons).
*
* Schedule parts must map to:
* minute [0-59], hour [0-23], day of month, month [1-12|JAN-DEC], day of week
* [1-7|MON-SUN], and an optional year.
*
* @see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cron
*/
class CronExpression
{
public const MINUTE = 0;
public const HOUR = 1;
public const DAY = 2;
public const MONTH = 3;
public const WEEKDAY = 4;
/** @deprecated */
public const YEAR = 5;
public const MAPPINGS = [
'@yearly' => '0 0 1 1 *',
'@annually' => '0 0 1 1 *',
'@monthly' => '0 0 1 * *',
'@weekly' => '0 0 * * 0',
'@daily' => '0 0 * * *',
'@midnight' => '0 0 * * *',
'@hourly' => '0 * * * *',
];
/**
* @var array CRON expression parts
*/
protected $cronParts;
/**
* @var FieldFactoryInterface CRON field factory
*/
protected $fieldFactory;
/**
* @var int Max iteration count when searching for next run date
*/
protected $maxIterationCount = 1000;
/**
* @var array Order in which to test of cron parts
*/
protected static $order = [
self::YEAR,
self::MONTH,
self::DAY,
self::WEEKDAY,
self::HOUR,
self::MINUTE,
];
/**
* @var array<string, string>
*/
private static $registeredAliases = self::MAPPINGS;
/**
* Registered a user defined CRON Expression Alias.
*
* @throws LogicException If the expression or the alias name are invalid
* or if the alias is already registered.
*/
public static function registerAlias(string $alias, string $expression): void
{
try {
new self($expression);
} catch (InvalidArgumentException $exception) {
throw new LogicException("The expression `$expression` is invalid", 0, $exception);
}
$shortcut = strtolower($alias);
if (1 !== preg_match('/^@\w+$/', $shortcut)) {
throw new LogicException("The alias `$alias` is invalid. It must start with an `@` character and contain alphanumeric (letters, numbers, regardless of case) plus underscore (_).");
}
if (isset(self::$registeredAliases[$shortcut])) {
throw new LogicException("The alias `$alias` is already registered.");
}
self::$registeredAliases[$shortcut] = $expression;
}
/**
* Unregistered a user defined CRON Expression Alias.
*
* @throws LogicException If the user tries to unregister a built-in alias
*/
public static function unregisterAlias(string $alias): bool
{
$shortcut = strtolower($alias);
if (isset(self::MAPPINGS[$shortcut])) {
throw new LogicException("The alias `$alias` is a built-in alias; it can not be unregistered.");
}
if (!isset(self::$registeredAliases[$shortcut])) {
return false;
}
unset(self::$registeredAliases[$shortcut]);
return true;
}
/**
* Tells whether a CRON Expression alias is registered.
*/
public static function supportsAlias(string $alias): bool
{
return isset(self::$registeredAliases[strtolower($alias)]);
}
/**
* Returns all registered aliases as an associated array where the aliases are the key
* and their associated expressions are the values.
*
* @return array<string, string>
*/
public static function getAliases(): array
{
return self::$registeredAliases;
}
/**
* @deprecated since version 3.0.2, use __construct instead.
*/
public static function factory(string $expression, FieldFactoryInterface $fieldFactory = null): CronExpression
{
/** @phpstan-ignore-next-line */
return new static($expression, $fieldFactory);
}
/**
* Validate a CronExpression.
*
* @param string $expression the CRON expression to validate
*
* @return bool True if a valid CRON expression was passed. False if not.
*/
public static function isValidExpression(string $expression): bool
{
try {
new CronExpression($expression);
} catch (InvalidArgumentException $e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Parse a CRON expression.
*
* @param string $expression CRON expression (e.g. '8 * * * *')
* @param null|FieldFactoryInterface $fieldFactory Factory to create cron fields
* @throws InvalidArgumentException
*/
public function __construct(string $expression, FieldFactoryInterface $fieldFactory = null)
{
$shortcut = strtolower($expression);
$expression = self::$registeredAliases[$shortcut] ?? $expression;
$this->fieldFactory = $fieldFactory ?: new FieldFactory();
$this->setExpression($expression);
}
/**
* Set or change the CRON expression.
*
* @param string $value CRON expression (e.g. 8 * * * *)
*
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException if not a valid CRON expression
*
* @return CronExpression
*/
public function setExpression(string $value): CronExpression
{
$split = preg_split('/\s/', $value, -1, PREG_SPLIT_NO_EMPTY);
Assert::isArray($split);
$notEnoughParts = \count($split) < 5;
$questionMarkInInvalidPart = array_key_exists(0, $split) && $split[0] === '?'
|| array_key_exists(1, $split) && $split[1] === '?'
|| array_key_exists(3, $split) && $split[3] === '?';
$tooManyQuestionMarks = array_key_exists(2, $split) && $split[2] === '?'
&& array_key_exists(4, $split) && $split[4] === '?';
if ($notEnoughParts || $questionMarkInInvalidPart || $tooManyQuestionMarks) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException(
$value . ' is not a valid CRON expression'
);
}
$this->cronParts = $split;
foreach ($this->cronParts as $position => $part) {
$this->setPart($position, $part);
}
return $this;
}
/**
* Set part of the CRON expression.
*
* @param int $position The position of the CRON expression to set
* @param string $value The value to set
*
* @throws \InvalidArgumentException if the value is not valid for the part
*
* @return CronExpression
*/
public function setPart(int $position, string $value): CronExpression
{
if (!$this->fieldFactory->getField($position)->validate($value)) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException(
'Invalid CRON field value ' . $value . ' at position ' . $position
);
}
$this->cronParts[$position] = $value;
return $this;
}
/**
* Set max iteration count for searching next run dates.
*
* @param int $maxIterationCount Max iteration count when searching for next run date
*
* @return CronExpression
*/
public function setMaxIterationCount(int $maxIterationCount): CronExpression
{
$this->maxIterationCount = $maxIterationCount;
return $this;
}
/**
* Get a next run date relative to the current date or a specific date
*
* @param string|\DateTimeInterface $currentTime Relative calculation date
* @param int $nth Number of matches to skip before returning a
* matching next run date. 0, the default, will return the
* current date and time if the next run date falls on the
* current date and time. Setting this value to 1 will
* skip the first match and go to the second match.
* Setting this value to 2 will skip the first 2
* matches and so on.
* @param bool $allowCurrentDate Set to TRUE to return the current date if
* it matches the cron expression.
* @param null|string $timeZone TimeZone to use instead of the system default
*
* @throws \RuntimeException on too many iterations
* @throws \Exception
*
* @return \DateTime
*/
public function getNextRunDate($currentTime = 'now', int $nth = 0, bool $allowCurrentDate = false, $timeZone = null): DateTime
{
return $this->getRunDate($currentTime, $nth, false, $allowCurrentDate, $timeZone);
}
/**
* Get a previous run date relative to the current date or a specific date.
*
* @param string|\DateTimeInterface $currentTime Relative calculation date
* @param int $nth Number of matches to skip before returning
* @param bool $allowCurrentDate Set to TRUE to return the
* current date if it matches the cron expression
* @param null|string $timeZone TimeZone to use instead of the system default
*
* @throws \RuntimeException on too many iterations
* @throws \Exception
*
* @return \DateTime
*
* @see \Cron\CronExpression::getNextRunDate
*/
public function getPreviousRunDate($currentTime = 'now', int $nth = 0, bool $allowCurrentDate = false, $timeZone = null): DateTime
{
return $this->getRunDate($currentTime, $nth, true, $allowCurrentDate, $timeZone);
}
/**
* Get multiple run dates starting at the current date or a specific date.
*
* @param int $total Set the total number of dates to calculate
* @param string|\DateTimeInterface|null $currentTime Relative calculation date
* @param bool $invert Set to TRUE to retrieve previous dates
* @param bool $allowCurrentDate Set to TRUE to return the
* current date if it matches the cron expression
* @param null|string $timeZone TimeZone to use instead of the system default
*
* @return \DateTime[] Returns an array of run dates
*/
public function getMultipleRunDates(int $total, $currentTime = 'now', bool $invert = false, bool $allowCurrentDate = false, $timeZone = null): array
{
$timeZone = $this->determineTimeZone($currentTime, $timeZone);
if ('now' === $currentTime) {
$currentTime = new DateTime();
} elseif ($currentTime instanceof DateTime) {
$currentTime = clone $currentTime;
} elseif ($currentTime instanceof DateTimeImmutable) {
$currentTime = DateTime::createFromFormat('U', $currentTime->format('U'));
} elseif (\is_string($currentTime)) {
$currentTime = new DateTime($currentTime);
}
Assert::isInstanceOf($currentTime, DateTime::class);
$currentTime->setTimezone(new DateTimeZone($timeZone));
$matches = [];
for ($i = 0; $i < $total; ++$i) {
try {
$result = $this->getRunDate($currentTime, 0, $invert, $allowCurrentDate, $timeZone);
} catch (RuntimeException $e) {
break;
}
$allowCurrentDate = false;
$currentTime = clone $result;
$matches[] = $result;
}
return $matches;
}
/**
* Get all or part of the CRON expression.
*
* @param int|string|null $part specify the part to retrieve or NULL to get the full
* cron schedule string
*
* @return null|string Returns the CRON expression, a part of the
* CRON expression, or NULL if the part was specified but not found
*/
public function getExpression($part = null): ?string
{
if (null === $part) {
return implode(' ', $this->cronParts);
}
if (array_key_exists($part, $this->cronParts)) {
return $this->cronParts[$part];
}
return null;
}
/**
* Gets the parts of the cron expression as an array.
*
* @return string[]
* The array of parts that make up this expression.
*/
public function getParts()
{
return $this->cronParts;
}
/**
* Helper method to output the full expression.
*
* @return string Full CRON expression
*/
public function __toString(): string
{
return (string) $this->getExpression();
}
/**
* Determine if the cron is due to run based on the current date or a
* specific date. This method assumes that the current number of
* seconds are irrelevant, and should be called once per minute.
*
* @param string|\DateTimeInterface $currentTime Relative calculation date
* @param null|string $timeZone TimeZone to use instead of the system default
*
* @return bool Returns TRUE if the cron is due to run or FALSE if not
*/
public function isDue($currentTime = 'now', $timeZone = null): bool
{
$timeZone = $this->determineTimeZone($currentTime, $timeZone);
if ('now' === $currentTime) {
$currentTime = new DateTime();
} elseif ($currentTime instanceof DateTime) {
$currentTime = clone $currentTime;
} elseif ($currentTime instanceof DateTimeImmutable) {
$currentTime = DateTime::createFromFormat('U', $currentTime->format('U'));
} elseif (\is_string($currentTime)) {
$currentTime = new DateTime($currentTime);
}
Assert::isInstanceOf($currentTime, DateTime::class);
$currentTime->setTimezone(new DateTimeZone($timeZone));
// drop the seconds to 0
$currentTime->setTime((int) $currentTime->format('H'), (int) $currentTime->format('i'), 0);
try {
return $this->getNextRunDate($currentTime, 0, true)->getTimestamp() === $currentTime->getTimestamp();
} catch (Exception $e) {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Get the next or previous run date of the expression relative to a date.
*
* @param string|\DateTimeInterface|null $currentTime Relative calculation date
* @param int $nth Number of matches to skip before returning
* @param bool $invert Set to TRUE to go backwards in time
* @param bool $allowCurrentDate Set to TRUE to return the
* current date if it matches the cron expression
* @param string|null $timeZone TimeZone to use instead of the system default
*
* @throws \RuntimeException on too many iterations
* @throws Exception
*
* @return \DateTime
*/
protected function getRunDate($currentTime = null, int $nth = 0, bool $invert = false, bool $allowCurrentDate = false, $timeZone = null): DateTime
{
$timeZone = $this->determineTimeZone($currentTime, $timeZone);
if ($currentTime instanceof DateTime) {
$currentDate = clone $currentTime;
} elseif ($currentTime instanceof DateTimeImmutable) {
$currentDate = DateTime::createFromFormat('U', $currentTime->format('U'));
} elseif (\is_string($currentTime)) {
$currentDate = new DateTime($currentTime);
} else {
$currentDate = new DateTime('now');
}
Assert::isInstanceOf($currentDate, DateTime::class);
$currentDate->setTimezone(new DateTimeZone($timeZone));
// Workaround for setTime causing an offset change: https://bugs.php.net/bug.php?id=81074
$currentDate = DateTime::createFromFormat("!Y-m-d H:iO", $currentDate->format("Y-m-d H:iP"), $currentDate->getTimezone());
if ($currentDate === false) {
throw new \RuntimeException('Unable to create date from format');
}
$currentDate->setTimezone(new DateTimeZone($timeZone));
$nextRun = clone $currentDate;
// We don't have to satisfy * or null fields
$parts = [];
$fields = [];
foreach (self::$order as $position) {
$part = $this->getExpression($position);
if (null === $part || '*' === $part) {
continue;
}
$parts[$position] = $part;
$fields[$position] = $this->fieldFactory->getField($position);
}
if (isset($parts[self::DAY]) && isset($parts[self::WEEKDAY])) {
$domExpression = sprintf('%s %s %s %s *', $this->getExpression(0), $this->getExpression(1), $this->getExpression(2), $this->getExpression(3));
$dowExpression = sprintf('%s %s * %s %s', $this->getExpression(0), $this->getExpression(1), $this->getExpression(3), $this->getExpression(4));
$domExpression = new self($domExpression);
$dowExpression = new self($dowExpression);
$domRunDates = $domExpression->getMultipleRunDates($nth + 1, $currentTime, $invert, $allowCurrentDate, $timeZone);
$dowRunDates = $dowExpression->getMultipleRunDates($nth + 1, $currentTime, $invert, $allowCurrentDate, $timeZone);
if ($parts[self::DAY] === '?' || $parts[self::DAY] === '*') {
$domRunDates = [];
}
if ($parts[self::WEEKDAY] === '?' || $parts[self::WEEKDAY] === '*') {
$dowRunDates = [];
}
$combined = array_merge($domRunDates, $dowRunDates);
usort($combined, function ($a, $b) {
return $a->format('Y-m-d H:i:s') <=> $b->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
});
if ($invert) {
$combined = array_reverse($combined);
}
return $combined[$nth];
}
// Set a hard limit to bail on an impossible date
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->maxIterationCount; ++$i) {
foreach ($parts as $position => $part) {
$satisfied = false;
// Get the field object used to validate this part
$field = $fields[$position];
// Check if this is singular or a list
if (false === strpos($part, ',')) {
$satisfied = $field->isSatisfiedBy($nextRun, $part, $invert);
} else {
foreach (array_map('trim', explode(',', $part)) as $listPart) {
if ($field->isSatisfiedBy($nextRun, $listPart, $invert)) {
$satisfied = true;
break;
}
}
}
// If the field is not satisfied, then start over
if (!$satisfied) {
$field->increment($nextRun, $invert, $part);
continue 2;
}
}
// Skip this match if needed
if ((!$allowCurrentDate && $nextRun == $currentDate) || --$nth > -1) {
$this->fieldFactory->getField(self::MINUTE)->increment($nextRun, $invert, $parts[self::MINUTE] ?? null);
continue;
}
return $nextRun;
}
// @codeCoverageIgnoreStart
throw new RuntimeException('Impossible CRON expression');
// @codeCoverageIgnoreEnd
}
/**
* Workout what timeZone should be used.
*
* @param string|\DateTimeInterface|null $currentTime Relative calculation date
* @param string|null $timeZone TimeZone to use instead of the system default
*
* @return string
*/
protected function determineTimeZone($currentTime, ?string $timeZone): string
{
if (null !== $timeZone) {
return $timeZone;
}
if ($currentTime instanceof DateTimeInterface) {
return $currentTime->getTimezone()->getName();
}
return date_default_timezone_get();
}
}
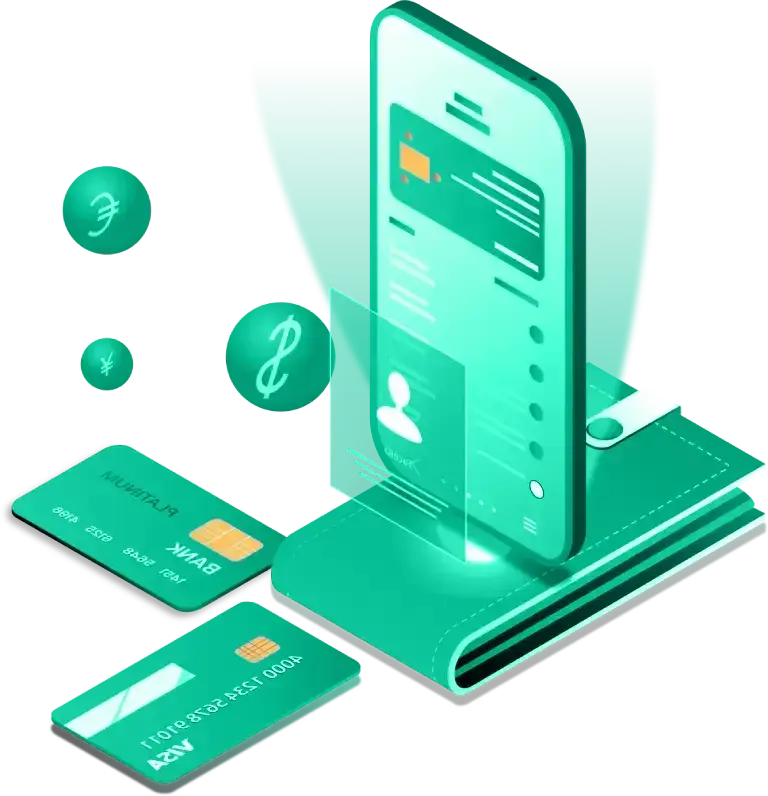
How it Works

Getting started with NFC Pay is simple and quick. Register your account, add your cards, and you're ready to make payments in no time. Whether you're paying at a store, sending money to a friend, or managing your merchant transactions, NFC Pay makes it easy and secure.
Download the NFC Pay app and sign up with your email or phone number. Complete the registration process by verifying your identity, and set up your secure PIN to protect your account.
Link your debit or credit cards to your NFC Pay wallet. Simply scan your card or enter the details manually, and you’re set to load funds, shop, and pay with ease.
To pay, simply tap your phone or scan the QR code at checkout. You can also transfer money to other users with a few taps. Enjoy fast, contactless payments with top-notch security.

Security System

NFC Pay prioritizes your security with advanced features that safeguard every transaction. From SMS or email verification to end-to-end encryption, we've implemented robust measures to ensure your data is always protected. Our security systems are designed to prevent unauthorized access and provide you with a safe and reliable payment experience.

Receive instant alerts for every transaction to keep track of your account activities.

Verify your identity through our Know Your Customer process to prevent fraud and enhance security.
Dramatically supply transparent backward deliverables before caward comp internal or "organic" sources.

All your data and transactions are encrypted, ensuring that your sensitive information remains private.

Monitor unusual activity patterns to detect and prevent suspicious behavior in real-time.
Why Choice Us

With NFC Pay, you get a trusted platform backed by proven expertise and a commitment to quality. We put our customers first, offering innovative solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring every transaction is secure, swift, and seamless.
Our team brings years of experience in the digital payments industry to provide reliable services.
We prioritize excellence, ensuring that every aspect of our platform meets the highest standards.
Your needs drive our solutions, and we are dedicated to delivering a superior user experience.
We continuously evolve, integrating the latest technologies to enhance your payment experience.
Testimonial Section

Hear from our users who trust NFC Pay for their everyday transactions. Our commitment to security, ease of use, and exceptional service shines through in their experiences. See why our clients choose NFC Pay for their payment needs and how it has transformed the way they manage their finances.
App Section

Unlock the full potential of NFC Pay by downloading our app, designed to bring secure, swift, and smart transactions to your fingertips. Whether you're paying at a store, transferring money to friends, or managing your business payments, the NFC Pay app makes it effortless. Available on both iOS and Android, it's your all-in-one solution for convenient and reliable digital payments. Download now and experience the future of payments!
